Abstract
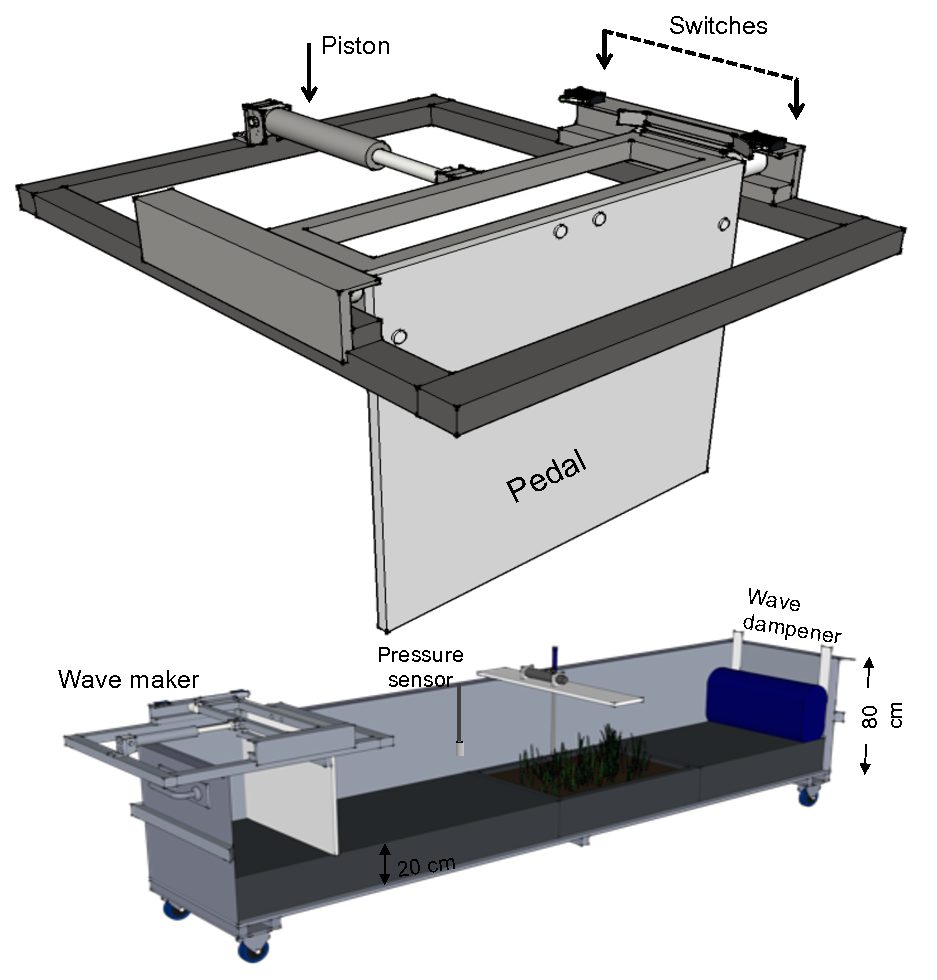
Wave flume facilities that are primarily designed for engineering studies are often complex and expensive to operate, and hence not ideal for long-term replicated experiments as commonly used in biology. This study describes a low-cost small wave flume that can be used for biological purposes using fresh or seawater with or without sediment.
The wave flume can be used as a mesocosm to study interactions between wave hydrodynamics and benthic organisms in aquatic ecosystems. The low-costs wave maker (less than 2000 USD) allows for experimental setups which can be easily replicated and used for longer-term studies; hence the term wave mesocosm. Waves were generated with a pneumatic piston and wave heights ranged between 3-6 cm. Maximum orbital flow velocities ranged between 10-50 cm s-1 representing shallow coastal areas with a short fetch.
The system can generate both regular waves (i.e., the wave period and orbital velocity remains constant), using a wave absorber, and irregular waves (i.e., varying wave period and orbital velocity) using a fast push and slow pull motion of the wave paddle. This wave mesocosm system is particularly useful in biogeomorphology to quantify interactions between organisms, sediment and hydrodynamics and for aquatic ecologist aiming to simulate realistic bed shear stress where short and long-term experiments (weeks-months) can be replicated.
Cire as: Infantes E, de Smit J, Tamarit E, Bouma TJ (2021) Making realistic wave climates in low-cost wave-mesocosms: a new tool for experimental ecology & biogeomorphology. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 19:317-330. DOI: 10.1002/lom3.10425