ABSTRACT
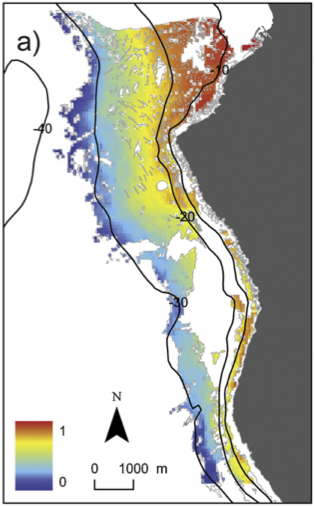
A spatially-explicit predictive model was developed for the cover of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica in a marine protected area (MPA) at Palma Bay (NW Mediterranean). A low-cost, novel drop camera system was designed and used to acquire standardized images that were used for estimating P. oceanica cover.
A simple, semi-quantitative cover index through visual inspection allowed robust estimates that are free of between-observer bias. A Bayesian kriging approach was implemented through a hierarchical model for non-Gaussian data. The map that was produced is a good match to a previous map of the presence–absence of P. oceanica that was produced by combining side scan sonar and aerial photography.
The influence of bathymetry, near-bottom orbital velocities (Ub) and slope on cover distribution were evaluated using a generalized linear model, while taking into account the spatial dependence between observations. We found that the important environmental variables were depth and Ub, while no effect of slope was found. The approach used here allowed us to not only map the cover of Posidonia oceanica but also to provide spatial-explicit information of prediction uncertainty.